The Differences Between UVA1 and PUVA
When you think of targeted phototherapy, you would first have to consider its main purpose – to target specific, infected spots so that areas of the body that are not infected will not get the unnecessary treatment or exposure it wouldn’t otherwise need.
Then we go into the intensity and penetration of the light treatments. Phototherapy involves ultraviolet lights. There are 2 popular targeted phototherapy treatments commonly used in the market: UVA1 and PUVA.
What is UVA1?
UVA1 is a high intensity, long-wavelength, ultraviolet light. These lights are typically used in phototherapy to treat a large number of chronic skin diseases. UVA1 treatments penetrate the skin more deeply than others. It induces the decomposition of collagen and gelatin, T-cell death, and depletion of Langerhans and mast cells in the dermis layer of the skin. This treatment also stimulates the skin cells to undergo neovascularization. This means that the treatment promotes the development of functional microvascular networks or blood vessels.
The UVA1 treatment has shown significant results when treating the following illnesses:
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is better known as atopic eczema which consists of inflamed red patches of skin that can be itchy, cracked and scaly.
Morphea
Morphea is a similar condition that presents as painless discolorations of the skin.
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is a rare type of cancer that begins in the white blood cells and attacks the skin.
Mastocytosis
Mastocytosis is a disorder that is seen in both children and adults. This condition is the result of too many mast cells being present in the body. Mast cells are typically found in the skin, lymph nodes, internal organs, and the lining of the stomach, lung and intestine.
Multiple inflammatory and sclerotic skin diseases have shown beneficial effects from UVA1 treatment.
UVA1 used to be conducted with a metal halide lamp and a series of optical filters. However, the icetron lamp has changed that. For 8 foot tubes, the concentration is poor, but the lamp used by Theralight is better than the metal halide. Metal halide lamps produce a great deal of heat. The Icetron lamp does not.
In many dermatitis cases, particularly sclerotic skin diseases, collagen metabolism, autoimmune activity, and vascular irregularity are responsible for the development of the condition. Since UVA1 photons are the deepest penetrating form of UV therapy they are able to disrupt these systems and halt the development of these illnesses.
UVA1 accomplishes this by encouraging the dissolution of collagen, skin T-cells and cytokines while promoting the growth of new vascular tissue in the afflicted regions.
Side Effects of UVA1
The side effects of UVA1 are fewer than those seen with other phototherapy techniques. Many UV treatments result in burns but these are less common with UVA1. Tanning is the most common side effect and this is an effect of almost all phototherapy. It has also been reported that this treatment reactivated herpes simplex virus. Chronic side effects include photo-aging and photo-carcinogenesis. Skin cancer development was usually coupled with other treatments that also increase the risk of developing cancer.
What is PUVA?
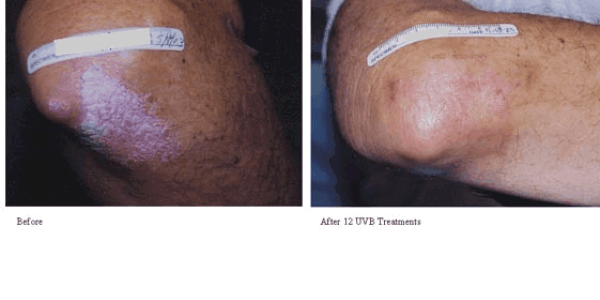
PUVA is a combination of long-wave ultraviolet radiation (UVA) and psoralen (P). This treatment is commonly used for psoriasis and other severe skin conditions. Psoralen is a drug that is often taken by mouth that makes the disease more sensitive to ultraviolet light. This allows the UVA light to affect eh diseased tissue.
This treatment is usually done 2-3 times a week for 12-15 weeks depending on the severity of the condition. It is never on consecutive days and maintenance therapy is often needed once a week.
Side Effects of PUVA
Side effects of this treatment can include:
• Headache
• Dizziness
• Skin burn and blisters
• Nausea
• Redness of the skin
• Itching
• Stinging sensation
• Tanning or darkening of the skin
Tanning side effects occur in every case because any UV treatment of the skin causes a darkening of the melatonin in the dermis. For this treatment in particular, nausea is the most common reason for halting treatment. Lowering the dose of Psoralen or using ginger capsules may help with the nausea and allow the treatments to continue. The rest of the potential side effects are largely temporary.
Patients that have undergone PUVA are at an increased risk of developing squamous cell skin cancer which can be treated with a minor surgery. It is also possible that PUVA puts patients at an increased risk of developing melanoma skin cancer as well but the development of this cancer requires a large volume of treatments. PUVA will make the skin look older, a side effect called photo-aging and can cause the development of white and brown spots on the skin.
It is vital that the eyes be protected during PUVA treatments as these can cause cataracts to form on the eyes otherwise. UVA absorbing sunglasses must also be worn for 24 hours following a treatment session and sunlight exposure for the skin must be completely avoided for at least 24 hours.
The treatment is completed by having the patient stand in a lightbox with the affected area exposed for 1-10 minutes, the length depends on the treatment level necessary and often begins as a small time period and is increased slowly over the course of the treatment schedule.
Alternative PUVA treatments can include the patient being soaked in a tub with a solution that makes the diseased tissue more vulnerable to UV light. After soaking in the tub for a period of time they are exposed to UV light as in the other treatments. This form of PUVA appears to have the same sort of side effects as the PUVA that is completed with the use of oral medications.
Differences between UVA1 and PUVA
While the main way in which these treatments are conducted is different, the diseases they are often used to treat vary as well. PUVA is commonly used to treat psoriasis while UVA1 is unable to address this issue because of the treatment costs.
Psoriasis often requires the treatment of large areas of the body if not all of the body. This is easier to accomplish and more cost effective with PUVA as UVA1 would require multiple treatments in order to address all of the problem areas and quickly becomes cost prohibited. Aside from psoriasis, there treatments are both used to address other chronic skin conditions and inflammations.
While the illnesses that these treatments are used to address are similar, their most common side effects are similar as well. Tanning is a guaranteed side effect of any exposure of the skin to UV light which is used in both of these treatments.
Both treatments result in the patients having increase susceptibility to develop a variety of skin cancers. While these cancers can be treated with minor surgeries, the increased risk of developing them in the first place is a potential result of both UVA1 and PUVA.